Explain the Differences Between Venous and Mixed Venous Blood Samples
Although it is the task of experts to suggest clear and simple guidelines there is a risk of reducing critical care to these simple recommendations. A model is presented involving a.

Mixed Venous Oxygen And Carbon Dioxide Content Deranged Physiology
Arterial blood is bright red colour but venous blood is dark maroon in colour.

. September 9 2019 Posted by DrSamanthi. Venous blood is the specimen of choice for most routine laboratory tests. A venous pH of 7 or lower for example predicted an arterial pH of 72 or lower in 98 of cases.
This figure shows the differences in mixed-venous saturation between the low- and high-dCO 2 groups on the ICU at time points 1 6 and 18 hours in the ICU in the patient cohort with central venous saturation 70. This generally produces an SvO 2 of 70. Annals of Emergency Medicine 1998.
Remember that the bicarbonate on a blood gas is a calculated value rather than a measured. However Plasmodium parasites are thought to be more concentrated in capillary than in venous blood. Whilst the use of venous blood is appropriate in a crossover design as any differences are within-subject our research has previously shown that arterialising venous samples by heating a.
Blood is a body fluid that delivers vital substances such as nutrients. What is the Difference Between Oxygenated and Deoxygenated Blood Comparison of Key Differences. Glucose measures at every moment absence of difference between.
Death none after it. A mixed venous blood gas is a sample aspirated from the most distal port of the PA catheter offering a mixture of inferior vena cava blood superior vena cava blood and the coronary sinuses. Central and mixed venous blood gases offer us a glimpse of whole-body oxygen extraction.
The normal mixed venous PO 2 PvO 2 is 40 mmHg. Shunt fraction is the calculated ratio of venous admixture to total cardiac output. Subject sample subject analyser and.
A short summary of this paper. Scvo2 is more conveniently measured and less risky than Svo2 measurement. Since venous blood gas is easy to sample from the peripheral veins or the central veins in patients with central venous catheters it is a more comfortable and an easy procedure for some patients and the physicians.
Both capillary and venous blood samples have been interchangeably used for the diagnosis of malaria in Ethiopia. In cardiac arrest victims the disparity between arterial and venous values is even greater. The linear correlation between actual calculated arterial HCO3- and the measured venous CO2 was significant P less than 001.
Arterial Blood Arteries Carbon Dioxide Deoxygenated Blood Oxygen Oxygenated Blood Veins Venous Blood. Supporting this hypothesis the difference between Hb measured in capillary and venous blood has been found to be higher in males than females likely mediated by males higher overall body red blood cell count contrasted with the reduced hematocrit red cell count and Hb in their microvasculature system including their capillaries27 43 In the study of over 36000 paired. Mixed venous oxygen saturation after admission to the intensive care unit ICU.
In many studies a very good correlation has been shown between venous blood gas and the arterial blood gas. The bicarbonate HCO 3 correlates well between arterial and venous samples and similar to the pH will closely approximate the arterial values with a difference of 052-15 mmolL McCanny 2011 Kelly 2001 Malatesha 2007 Middleton 2006 Rang 2002. Hence selecting a sample source where parasites are more concentrated is indispensable approach in order to maximize the accuracy.
Venipuncture samples for venous CO2 content and chloride concentrations were obtained in 336 patients with arterial blood pH PaO2 PaCO2 and oxygen saturation determinations. Comparison of Arterial and Venous Blood Gas Values in the Initial Emergency Department Evaluation of Patients With Diabetic Ketoacidosis. Central venous oxygen saturation ScvO2 70 or mixed venous oxygen saturation SvO2 65 is recommended for both septic and non-septic patients.
If the PvO 2 rises above 60 mmHg the SvO 2 may rise to arterial saturation levels. The arterial blood is bright red in color and the venous blood is blackish red in color. Arterial blood travels through the left chamber of the heart whereas venous blood moves through the right chambers of the heart.
At times venous blood may be obtained using a vascular access device VAD such as a central venous pressure line or an IV start. Aspiration of air into the blood gas syringe during sampling or the presence of an air bubble are potential causes for false elevation of SvO 2. Thus the result is an average of venous blood.
Under conditions in which no gas exchange occurs across the mammalian lung a steady state difference between alveolar and mixed venous P CO 2 ΔP CO 2 was found the alveolar being higherThe ΔP CO 2 appeared to be related to the H and HCO 3 concentrations of the mixed venous blood and to the pulmonary blood flow rate. Venous admixture is that amount of mixed venous blood which would have to be added to ideal pulmonary end-capillary blood to explain the observed difference between pulmonary end-capillary PO 2 and arterial PO 2. What is Oxygenated Blood.
The blood is obtained by direct puncture to a vein most often located in the antecubital area of the arm or the back top of the hand. The main difference between arterial and venous blood is that arterial blood is oxygenated whereas venous blood is deoxygenated. Scvo2 measures central venous oxygen saturation level from veins draining the head and upper body while Svo2 measures mixed venous oxygen saturation from the lower half of the body.
For It is commonly stated that venous samples give slightly the venous samples there were four measurements per person in lower values than capillary samples and that these differences a 2 2 layout of sample and laboratory analyser resulting in can generally be ignored in the fasting state but after a meal or three variance components. Oxygenated blood refers to the blood that has been exposed to oxygen in the lungs. The key difference between arterial and venous blood gas is that arterial blood gas test uses a small blood sample drawn from an artery while venous blood gas test is a comparatively less painful test that uses a small blood sample drawn from a vein.
Full PDF Package Download Full PDF Package. During cardiac arrest tissue hypoxia is all but a certainty and is reflected by the lower pH and higher PCO 2 on the venous side. Venous and arterial glycaemia was rather rare.

Mixed Venous Oxygen And Carbon Dioxide Content Deranged Physiology
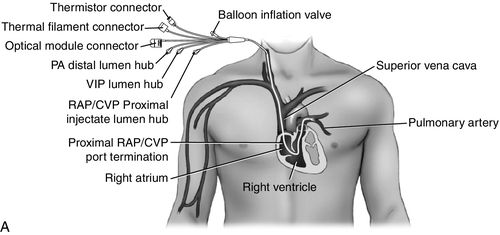
Venous Oxygen Saturation Monitoring Anesthesia Key

Mixed Venous Oxygen And Carbon Dioxide Content Deranged Physiology
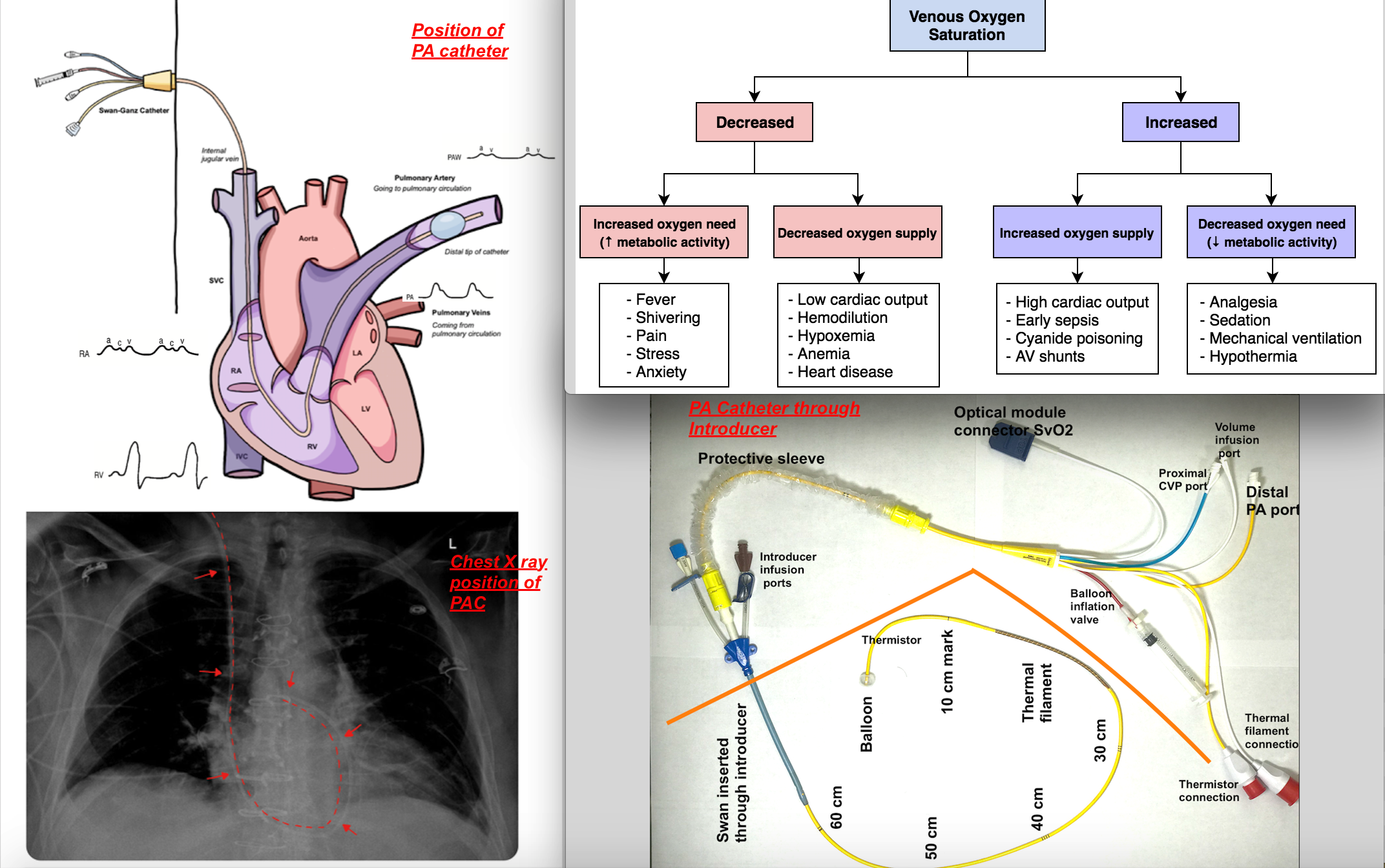
Anesthesia Monitoring Of Mixed Venous Saturation Article

Mixed Venous Oxygen And Carbon Dioxide Content Deranged Physiology
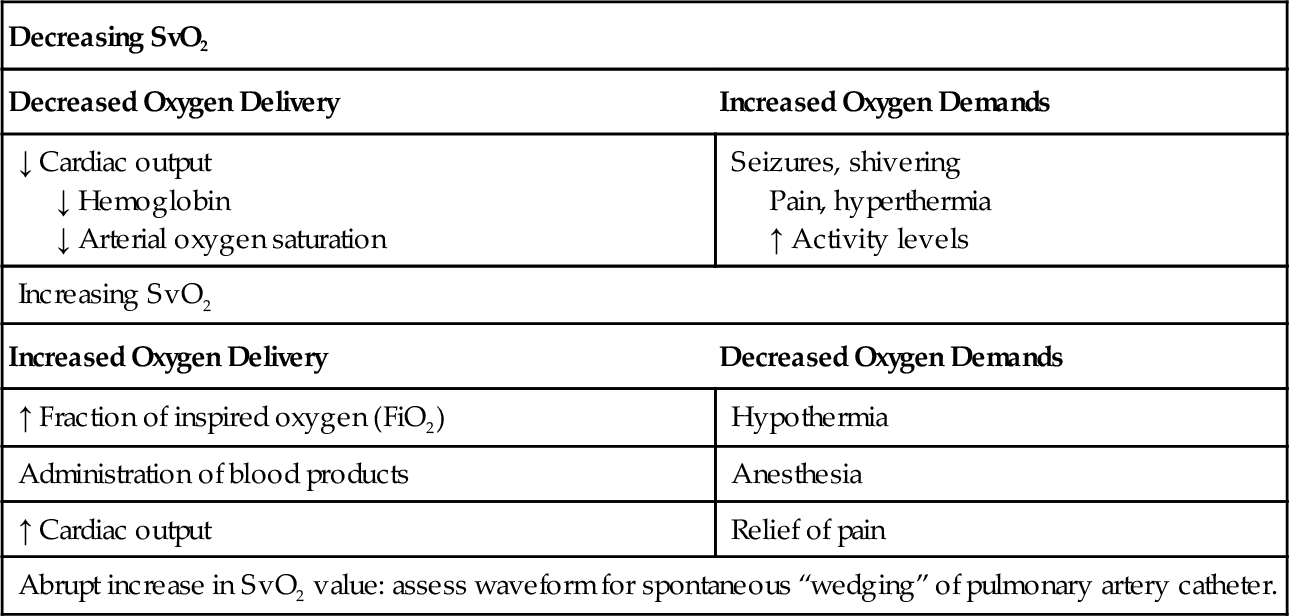
Venous Oxygen Saturation Monitoring Anesthesia Key

Pdf Central Venous Oxygenation For Mixed Venous Oxygen Saturation Semantic Scholar
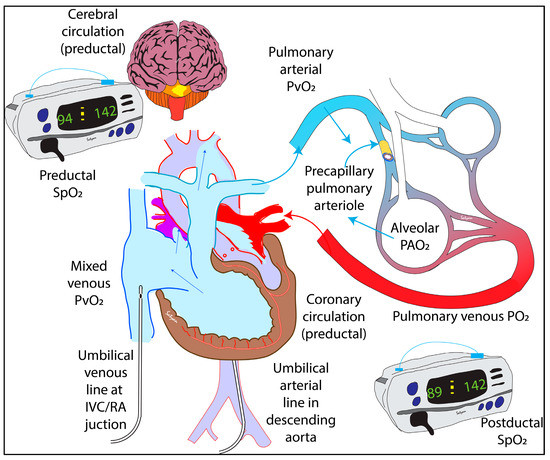
Children Free Full Text How Do We Monitor Oxygenation During The Management Of Pphn Alveolar Arterial Mixed Venous Oxygen Tension Or Peripheral Saturation Html

Mixed Venous Oxygen And Carbon Dioxide Content Deranged Physiology

Venous Blood An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Comparison Of Minimally And More Invasive Methods Of Determining Mixed Venous Oxygen Saturation Journal Of Cardiothoracic And Vascular Anesthesia
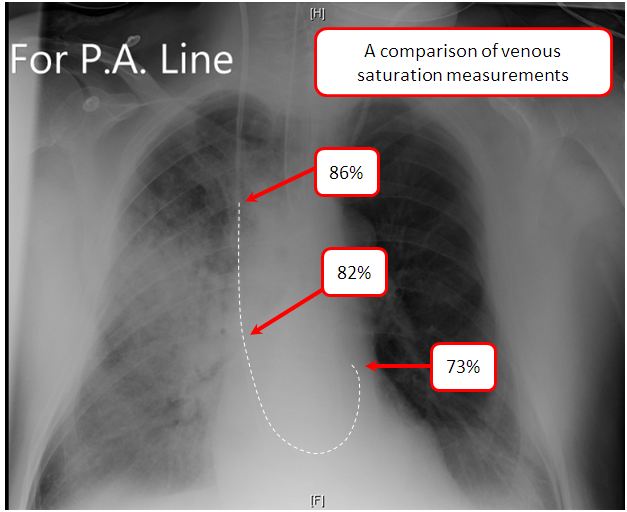
Mixed Venous Oxygen And Carbon Dioxide Content Deranged Physiology
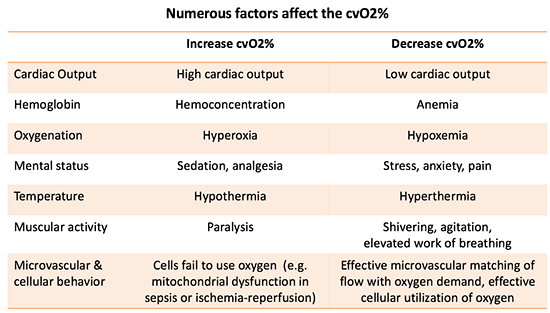
Pulmcrit Central Venous Oxygen Saturation Signal Or Noise

Practical Use Of Central And Mixed Venous Blood Gases Deranged Physiology
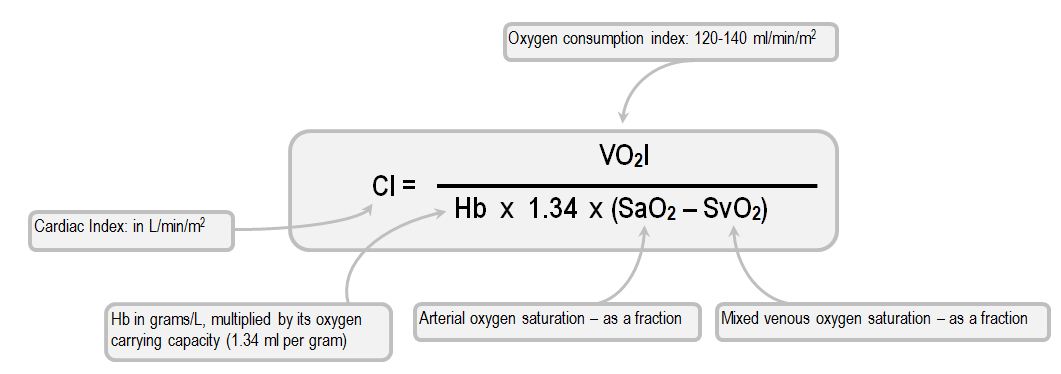
Practical Use Of Central And Mixed Venous Blood Gases Deranged Physiology

Pdf Central Venous Oxygenation For Mixed Venous Oxygen Saturation Semantic Scholar


Comments
Post a Comment